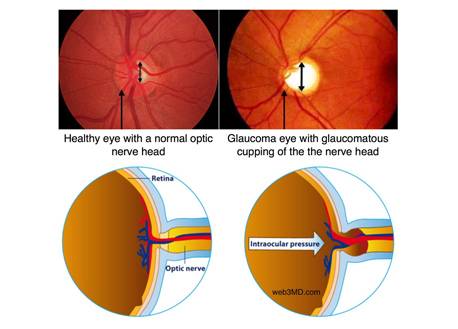
How is glaucoma diagnosed?
Glaucoma can be diagnosed with a routine examination or when a patient visits the doctor for the above-described symptoms.
Diagnose is confirmed by:
- Tonometry/eye pressure checkup: Normal eye pressure is 12-21 mm Hg. A rise in intraocular pressure is the highest risk factor for glaucoma.
- Optic nerve examination: By a special lens to check the nerve loss
- Pachymeter: Corneal thickness measurement to checkup for corrected intraocular pressure.
- Perimetry or computerized visual field testing: To check the subtle defect in field of vision which we are not aware of in routine day today life.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): A kind of scan of the optic nerve to evaluate nerve fibre layer thickness and also presence and extent of glaucoma damage.
- Fundus Photography: The photography of the optic nerve to check for progression or stability of glaucoma.